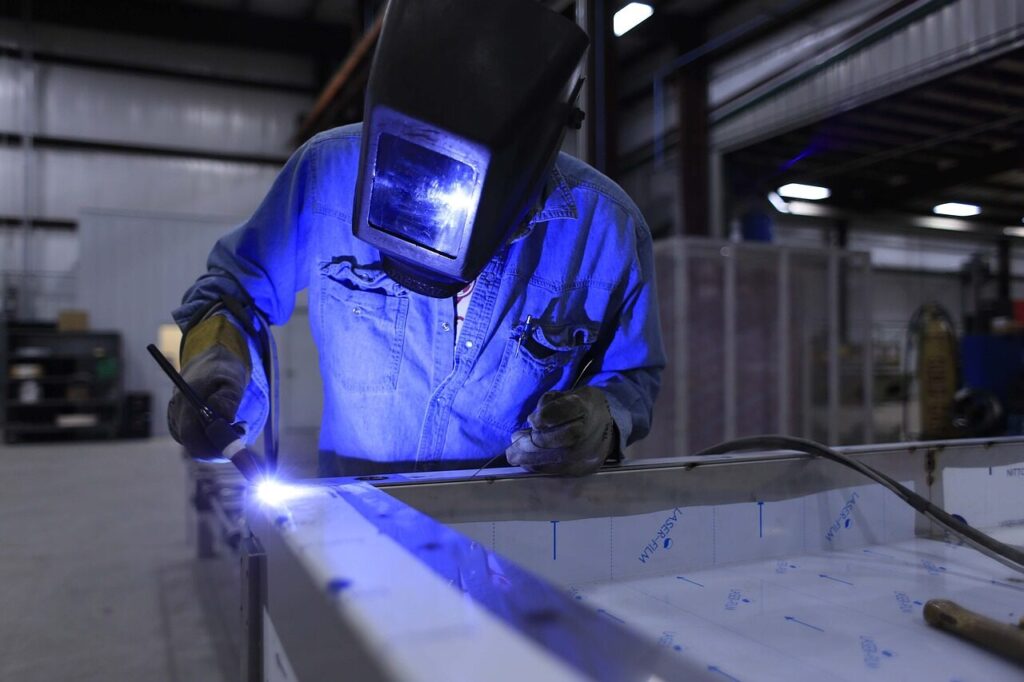
In modern manufacturing, the landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the pursuit of efficiency. One crucial aspect of this evolution is welding technology. From traditional methods to cutting-edge techniques, welding plays a pivotal role in shaping various industries. Here are the latest trends and applications of innovative welding solutions that are revolutionizing modern manufacturing processes.
Hydraulic Welding
Hydraulic welding is a specialized welding technique that utilizes hydraulic pressure to generate heat and join materials together. Unlike traditional welding methods that rely on electrical arcs or flames for heat generation, hydraulic welding operates by compressing a liquid, typically oil, to generate intense pressure, which in turn produces the required heat for welding. For hydraulic welding, exploring further at nabtescoprecision.com can help you discover advanced solutions tailored to your manufacturing needs. This process is particularly effective for welding thick materials or components with large surface areas, as the hydraulic force can be precisely controlled to ensure uniform heat distribution.
Laser Welding: Pushing the Boundaries of Possibilities
Laser welding represents a cutting-edge technology that offers several advantages over traditional welding methods. By harnessing the power of concentrated laser beams, manufacturers can achieve extremely precise and clean welds. This technique is particularly beneficial for welding materials with high thermal conductivity or those requiring minimal distortion. Additionally, laser welding enables faster processing speeds and can be easily automated, making it ideal for high-volume production environments.
Exceptional Precision
Laser welding offers unmatched precision, thanks to its concentrated energy beam that can be accurately controlled and focused on the weld seam. This precision results in minimal distortion and heat-affected zones, making it ideal for applications where tight tolerances are critical, such as medical device manufacturing or aerospace components. The ability to achieve precise welds also reduces the need for post-welding machining or finishing processes, saving time and resources in production.
Versatility in Material Compatibility
Laser welding exhibits exceptional versatility in joining various materials, including dissimilar metals and alloys, without the need for filler material. This capability is particularly advantageous in industries where multi-material assemblies are common, such as automotive manufacturing or electronics production. By eliminating the need for additional materials, laser welding streamlines the manufacturing process and reduces material costs, contributing to overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
High Processing Speeds
Laser welding enables rapid processing speeds compared to traditional welding methods, allowing for increased throughput and shorter production cycles. This accelerated processing capability is especially beneficial for high-volume manufacturing environments, where efficiency and productivity are paramount. Additionally, the ability to complete welds quickly reduces the risk of heat buildup and potential damage to sensitive components, ensuring consistent weld quality and reliability.
Friction Stir Welding: Joining Dissimilar Materials with Ease
Friction stir welding (FSW) is a revolutionary technique that enables the joining of dissimilar materials without the need for traditional fusion welding processes. Instead of melting the materials, FSW uses frictional heat and mechanical pressure to create a strong, solid-state bond. This method is particularly well-suited for lightweight alloys, such as aluminum and magnesium, which are commonly used in aerospace and automotive applications. FSW offers superior joint strength, improved fatigue resistance, and enhanced weld quality compared to conventional welding methods.
Unlocking Precision in High-Performance Applications
Electron beam welding (EBW) is a sophisticated process that utilizes a focused beam of high-velocity electrons to join metal components with exceptional precision. This technology is especially advantageous for welding thick or complex geometries where traditional methods may struggle. EBW produces narrow heat-affected zones and minimal distortion, making it ideal for critical applications in industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical devices. Additionally, EBW offers the ability to weld materials with high melting points, including refractory metals like titanium and tantalum.
Additive Manufacturing: Revolutionizing Production with 3D Printing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has transformed the landscape of modern manufacturing by enabling the creation of intricate geometries and complex components with unparalleled efficiency. While additive manufacturing encompasses various processes, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) and selective laser melting (SLM), it also includes metal 3D printing technologies capable of producing fully functional metal parts through selective laser sintering or electron beam melting. This approach offers flexibility in design, reduced material waste, and accelerated prototyping and production cycles.
Hybrid Welding: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid welding integrates multiple welding processes, such as laser welding and gas metal arc welding (GMAW), to capitalize on their respective strengths and overcome limitations. By combining heat sources, manufacturers can achieve improved weld penetration, enhanced control over weld morphology, and increased process flexibility. Hybrid welding is particularly beneficial for applications requiring a balance between speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness, offering a versatile solution for a wide range of manufacturing challenges.
Image source: https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-illuminated-room-320621/
Innovative welding solutions are driving significant advancements in modern manufacturing, enabling manufacturers to push the boundaries of what’s possible. From robotic welding systems that enhance precision and efficiency to cutting-edge techniques like laser welding and friction stir welding, the options are vast and diverse. By embracing these technologies, manufacturers can unlock new opportunities for innovation, improve product quality, and stay ahead in today’s competitive marketplace.