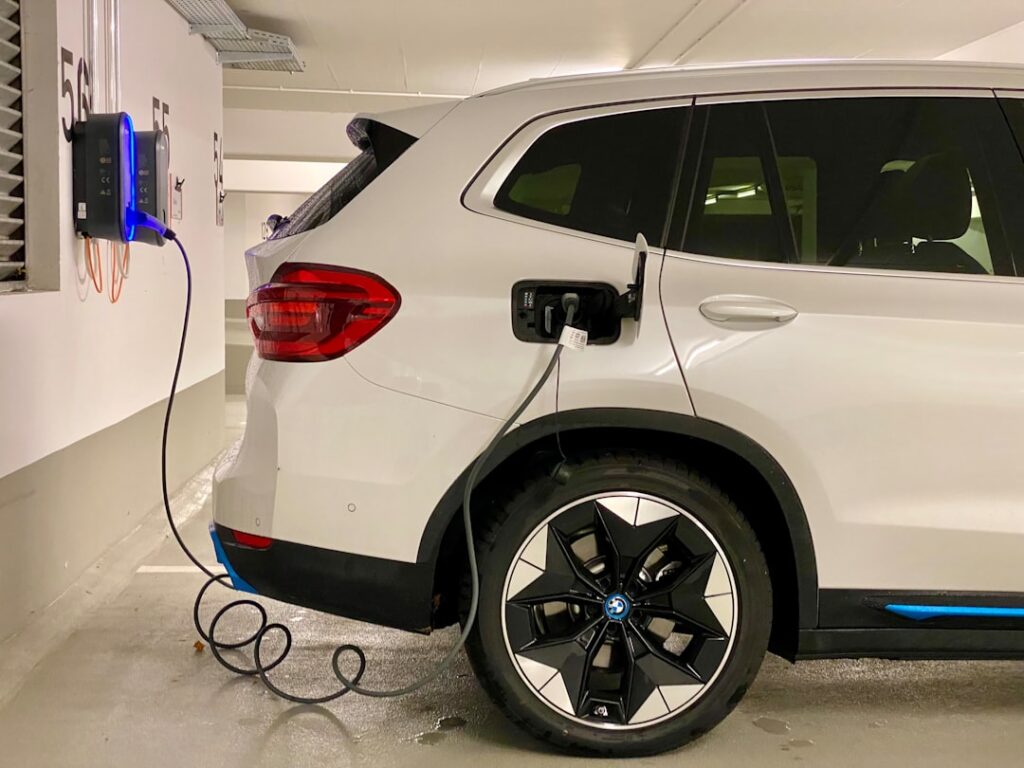
If you’ve recently leaped to eco-friendlier driving with an electric vehicle (EV), you know that owning one is not just about the thrill of silent acceleration – it’s also about charging the battery, and that part requires a little more consideration than a traditional trip to the gas station. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll walk you through the ins and outs of bringing an EV charging system right to your doorstep, ensuring you’re powered up and ready to ride at home.
Navigating the Maze of EV Charger Types
Before you can start plugging in, you’ll need to understand the types of EV chargers available. There are three primary levels – Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (DC Fast Charging) – each with pros and cons relating to charging speed and infrastructure requirements. Level 1 chargers are the slowest, offering about 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging, while Level 2 chargers, which typically require a 240-volt connection like a dryer or oven, can provide around 25 miles of range per hour.
Level 3 chargers, on the other hand, are commercial-grade units known as DC Fast Chargers, and they can replenish your EV’s battery far more quickly. However, they are cost-prohibitive and are typically not suitable for home use. For most residential EV owners, Level 2 chargers found at btcpower.com/products/ac-chargers-level-2 offer a great balance of speed and affordability. The charger you choose will depend on your vehicle’s compatibility and your daily driving needs. Thankfully, most electric cars come with a Level 1 charger, which can serve as a supplementary or backup charging solution.
Selecting the Right EV Charger for Your Needs
Once you’ve determined that a Level 2 charger is the right fit for your home, it’s time to pick a specific model. There is an array of manufacturers in the market, and their chargers vary not just in price but also in terms of features, warranty, and user-friendliness. Some chargers are smart chargers, which can be controlled via a smartphone app, scheduled to run overnight during off-peak electricity times, and even integrated with solar panels for an eco-double-whammy.
Consider the placement of your charger – it should be easy to access but out of the way of pedestrians and vehicles. If you park outside, you’ll also need a charger that’s weatherproof and durable. Look for a unit that’s both Ul-listed and tested for EV-readiness, ensuring that it meets strict safety standards and is compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles. Lastly, factor in the installation cost when budgeting for your new charger – a licensed electrician may be required to install the unit.
Understanding the Installation Process
Installing a Level 2 EV charging system is a job that usually requires a professional electrician. The process begins with a site assessment, where the electrician will check your home’s electrical panel to determine its capacity and the most feasible wiring route to where the charger will be installed. Oftentimes, the electrical panel will need to be upgraded to handle the additional load of your EV charger.
Next, a dedicated circuit will be installed, and if necessary, the electrician will run a new line from your electrical panel to the charger location. Once the wiring is set, the charger will be mounted on a wall or a standalone post. The installation process is generally straightforward, but it’s critical to have a professional conduct this work to ensure that everything is safely and correctly connected.
Cost and Incentives for Home EV Charging
The cost of installing a Level 2 EV charging system at home can vary significantly depending on your home’s electrical setup, the charger you’ve chosen, and local labor rates. On average, you can expect to pay anywhere from $500 to $2,000 for the installation, not including the cost of the charger itself. To alleviate this financial burden, there are numerous incentives available for EV charging installations.
Many utility companies offer rebates or other financial incentives to encourage the installation of residential EV chargers. Additionally, the federal government and some local authorities offer tax credits that can further offset the cost. These incentives can make the switch to home charging more affordable and, in some cases, can even cover most of the installation costs, turning what might seem like a hefty investment into a budget-friendly home improvement project.
Bringing an EV charging system to your home is an important step in the electrification of transportation. By understanding the different types of chargers, selecting the right one, navigating the installation process, and leveraging financial incentives, you can make the process smoother and more affordable. With a little effort and the right approach, you’ll soon be enjoying the convenience of home charging and the satisfaction of knowing you’re contributing to a cleaner, greener planet. Welcome to the electric revolution – you’re all set to plug in and lead the charge.